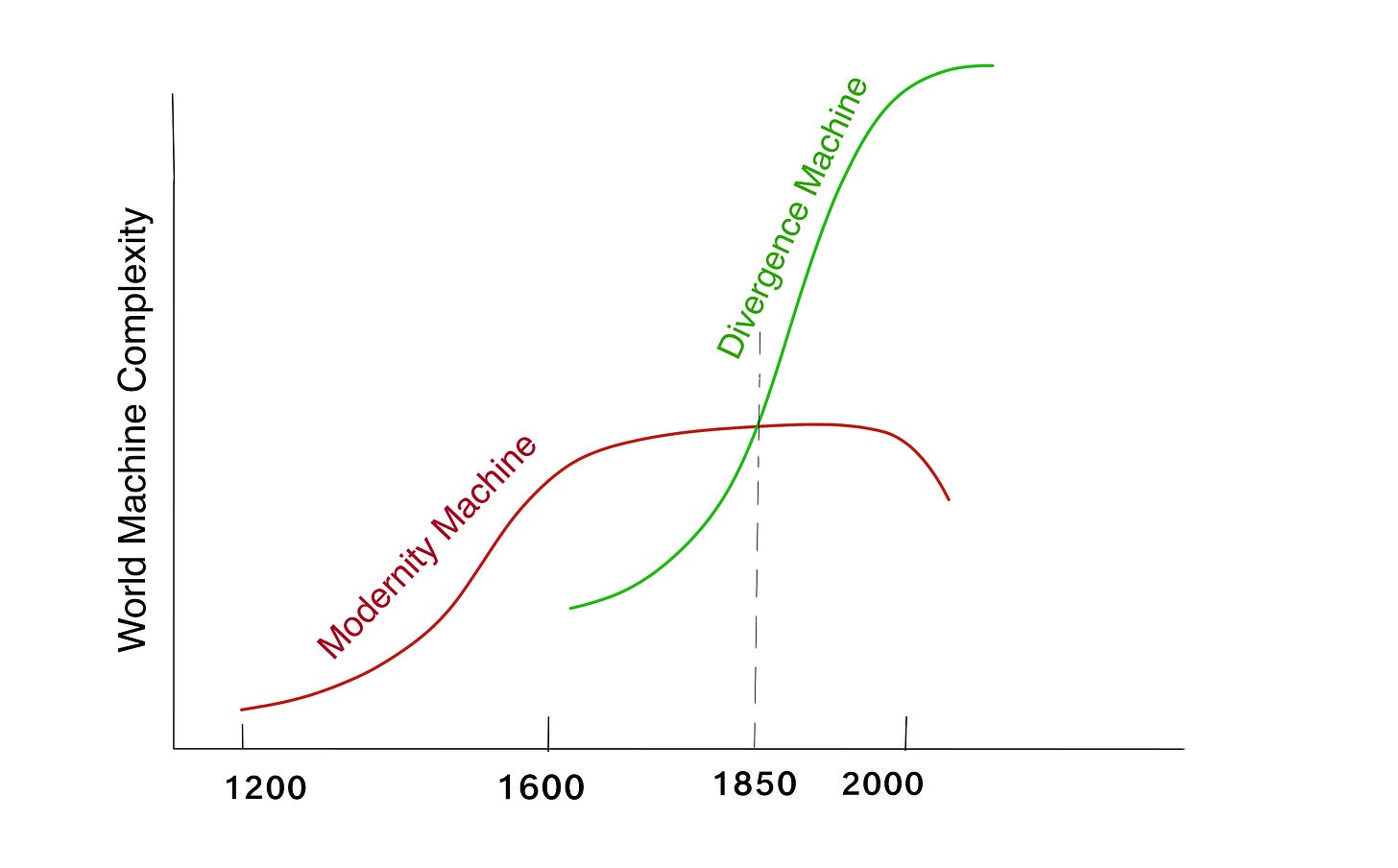
This the third and concluding part of my series with notes on the learnings from the 2025 Contraptions book club. Part I and Part II
traced the construction of the Modernity Machine between roughly 1200
and 1600: a civilization-scale contraption that converted medieval
heterogeneity into legible, interoperable order. By 1600, the machine
was complete in all essential respects. This concluding part addresses
what such completion actually meant, what the machine optimized for once
built, the contradictions it necessarily produced, and why those
contradictions could not be repaired from within.
The aim
is not to declare the “end of modernity,” but to close out a rough
analysis of the machine that took 400 years to build and turn on,
making modernity possible, and sustained it for another 400 years, being
patched in increasingly fragilizing ways along the way. And also to
explore why its very success post-1600 began forcing a slow phase
transition to a different kind of civilizational machinery which began
to get constructed around 1600, right when the Modernity Machine got
turned on. This machine, which I refer to as the Divergence Machine, is
being completed and turned on as we speak, even as the Modernity Machine
is starting to get decommissioned in bits and pieces worldwide. Here is
a teaser picture for the overarching thesis we’re developing here.
The 1600-2000 period and the Divergence Machine that emerged in that period will be the subject of the 2026 book club.
But let’s wrap up 2025 first.
You can catch up on the closing 2025 group discussion in this transcript. What follows is my personal wrap-up.
The
Modernity Machine did not optimize for truth, justice, progress, or
freedom—those were its legitimating narratives. What it optimized for,
relentlessly and across domains, was legibility: the ability to render
people, land, goods, time, belief, and violence enumerable, narratable,
and interoperable at scale.
Venice, in City of Fortune,
is not interesting because it was rich or republican, but because it
functioned as an early, tightly integrated legibility engine: maritime
logistics, double-entry bookkeeping, legal abstraction, diplomacy, and
intelligence-gathering fused into a self-reinforcing apparatus. Venice: A New History fills in the same picture from another angle: stability emerges not from ideology but from procedural compression.
The horse, in Raiders, Rulers, and Traders,
plays a parallel role across Eurasia: a biological technology that
collapses distance, standardizes military force, and forces political
units to scale or perish. The horse is legibility made kinetic.
Printing, in The Printing Revolution in Early Modern Europe,
completes the transition. Knowledge becomes reproducible independent of
context. Interpretation decouples from replication. Information density
explodes while shared meaning lags behind. The machine acquires a
memory that grows faster than any coordinating narrative.
1493
shows the planetary version of the same dynamic. The Columbian exchange
is not merely ecological or economic; it is a global synchronization
event. Previously isolated systems are forced into a single ledger. The
machine’s jurisdiction becomes planetary even as its capacity for
meaning remains local.
Seen this way, the Modernity Machine
is best understood as a civilization-scale compression algorithm. For
several centuries, the gains are extraordinary.
To understand what the machine displaced, it helps to look at relatively pristine end-of-medieval snapshots.
Majapahit
offers such a snapshot outside Europe: a highly developed but still
recognizably medieval empire, organized around courtly ritual, tributary
relations, and localized legitimacy, poised at the cusp of collapse
before modernity arrives in force. It represents a world not yet
reorganized by legibility, still governed by face-to-face sovereignty
and cosmological order.
Within Europe, The Age of Chivalry
performs a similar function. Chivalry appears not as romance but as a
fully articulated medieval coordination system—ethical, military, and
social—already straining under pressures it cannot metabolize. This is
medievalism at its most coherent, just before it becomes an anachronism.
These
snapshots matter because they show what modernity did not inherit:
localized legitimacy, narrative sufficiency, and bounded scale.
Once the Modernity Machine works, it produces three unavoidable byproducts.
First, excess agency. Feudal bonds dissolve, religious monopolies weaken, markets and cities proliferate. The Canterbury Tales and The Decameron
are early catalogs of proliferating voices and moral standpoints.
Social life becomes polyphonic. Coordination becomes harder because more
people can act.
Second, excess information. Printing destabilizes epistemic hierarchy. By Montaigne’s time, the educated individual is already drowning in books. The Complete Essays
read as field notes from the first generation to experience epistemic
overload. Skepticism is both a philosophical stance and a coping
mechanism.
Third, excess scale. Before European Hegemony and When Asia Was the World
make clear that global integration predates European dominance, but
modernity hardens integration into permanent structure. Local meaning
cannot survive planetary circulation intact.
The machine
creates more actors than it can integrate, more information than it can
interpret, and more scale than it can narrate.
The lesson of Giordano Bruno and the Hermetic Tradition
is not that Bruno foresaw modern pluralism. It is almost the opposite.
Bruno represents the last exuberant escape of medieval imagination—a
crackpot magician and memory-maven operating within an anachronistic
misunderstanding of Hermeticism as ancient Egyptian wisdom to
hallucinate a worldview of bullshit — indifferent to truth or falsity in
any modern empirical sense. His cosmological conclusions happened to
resonate sympathetically with Copernican implications, but for
fundamentally wrong reasons.
Bruno does not anticipate
modernity; he misunderstands it. His fate marks not the birth of a new
worldview, but the extinguishing of a freewheeling medieval mode
incompatible with both emerging authoritarian modernism, especially
ecclesiastical, and scientific empiricism. What survives of his
tradition—Rosicrucianism, Masonic esotericism—persists as fringe
subculture: culturally influential at times, intellectually irrelevant
to the main currents of modern thought.
Bruno is thus not an early modern prophet, but a terminal medieval outlier.
Similarly, Ibn Khaldun: An Intellectual Biography
should not be read as the story of a proto-sociologist ahead of his
time. That role is largely retrofitted by modern interpreters. In his
own context, Ibn Khaldun appears more plausibly as a kind of depressed
Arab Petrarch: a brilliant chronicler of decline and defender of
tradition, lamenting the absence of an Islamic renaissance rather than
inaugurating one.
His cyclical theory of dynasties does not
launch a new science of society; it records the exhaustion of an old
civilizational form. The importance of Ibn Khaldun here is diagnostic,
not genealogical. He documents a world failing to enter the Modernity
Machine at all, despite being in possession of many of the necessary
components.
By the early modern period, narrative itself begins to fail as a unifying technology. Don Quixote stands as the European bookend to The Age of Chivalry.
Quixote behaves impeccably within a dead symbolic system, and chaos
results. The novel demonstrates that inherited narratives no longer
synchronize action with reality.
Journey to the West
stages the same problem mythically. The Monkey King embodies pure
agency without moral center. Order is restored only through endless
improvisation, not closure. This is not premodern innocence but
recognition that containment now requires perpetual patching, a
condition whose outer story is told in 1493.
Utopia
remains the last sincere architectural drawing of the Modernity
Machine. It assumes total legibility, benevolent coordination, stable
universals, and obedient subjects. Even at publication, it is already
obsolete. The social, informational, and political conditions required
for utopia to function are precisely those modernity has destroyed in
creating itself.
Everything after Utopia
is retrofit to a completed civilizational machine, to patch problems
that began appearing almost immediately after it was turned on in 1600.
By
1600, the machine has crossed a complexity threshold. More law
increases rigidity without legitimacy. More reason fragments into
disciplines. More planning amplifies unintended consequences. More
morality polarizes rather than integrates.
This is not moral
failure or intellectual laziness. It is structural. The Modernity
Machine generates more differentiation than any universal framework can
absorb.
The Modernity Machine does not collapse, but a new
logic begins cohering at its periphery. Coordination shifts from
top-down design to nudging from the margins — and increasingly, everybody
is in the margins. Some just recognize it in 1600, while others are
only realizing it now in 2025. Legitimacy fragments. Meaning localizes.
Systems adapt without consensus. Civilization continues to
function—often remarkably well—while agreeing less and less about what
it is doing or why.
This is the phase transition. The
machine that made convergence possible gives way to a machine that
produces divergence as a default condition.
The Modernity
Machine has done its job. What follows is not its negation, but the
emergence of a Divergence Machine destined to replace it—a different
contraption, hot-swapped piecemeal for its predecessor over 400 years,
between 1600 and 2000. Optimized not for legibility and convergence, but
for proliferation, adaptation, and coexistence without closure. For divergence.
That is the story of 1600–2000, which we will tackle in 2026.
The picks for the first three months have been posted on the book club page if you want to get a head start. I’ll lay out the thesis in a January kickoff post.